July 2024
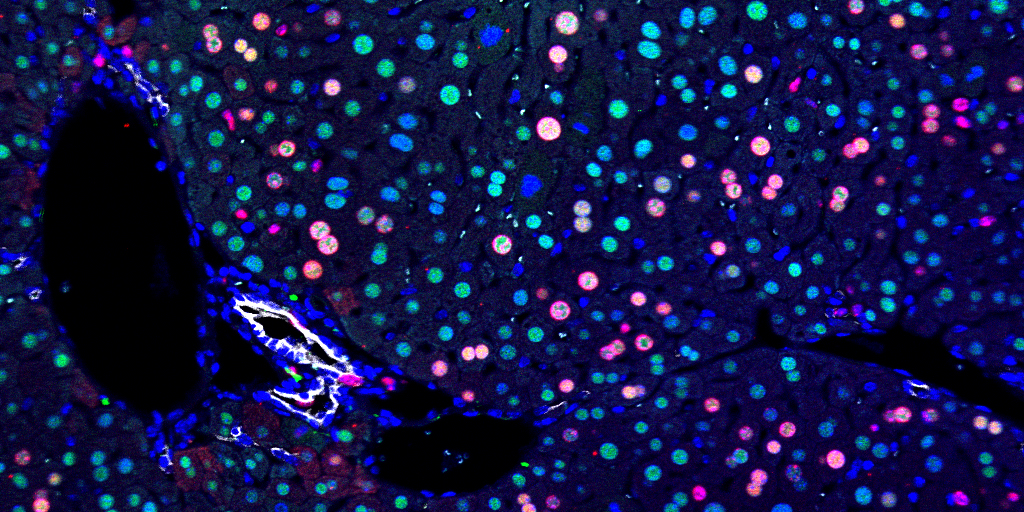
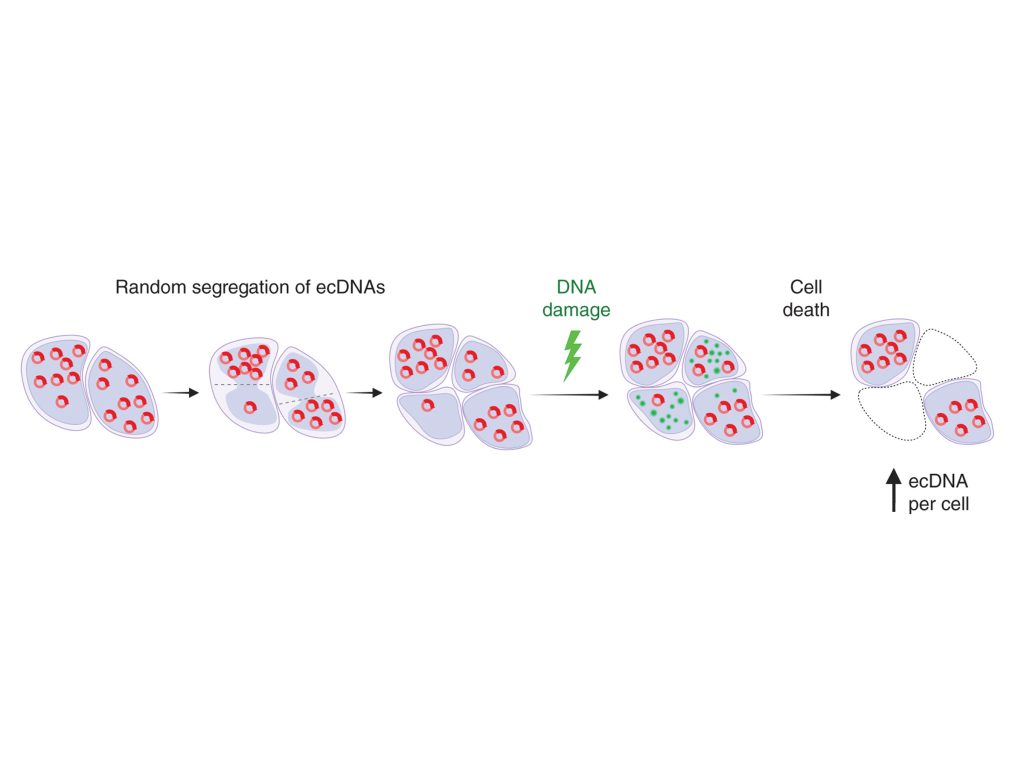
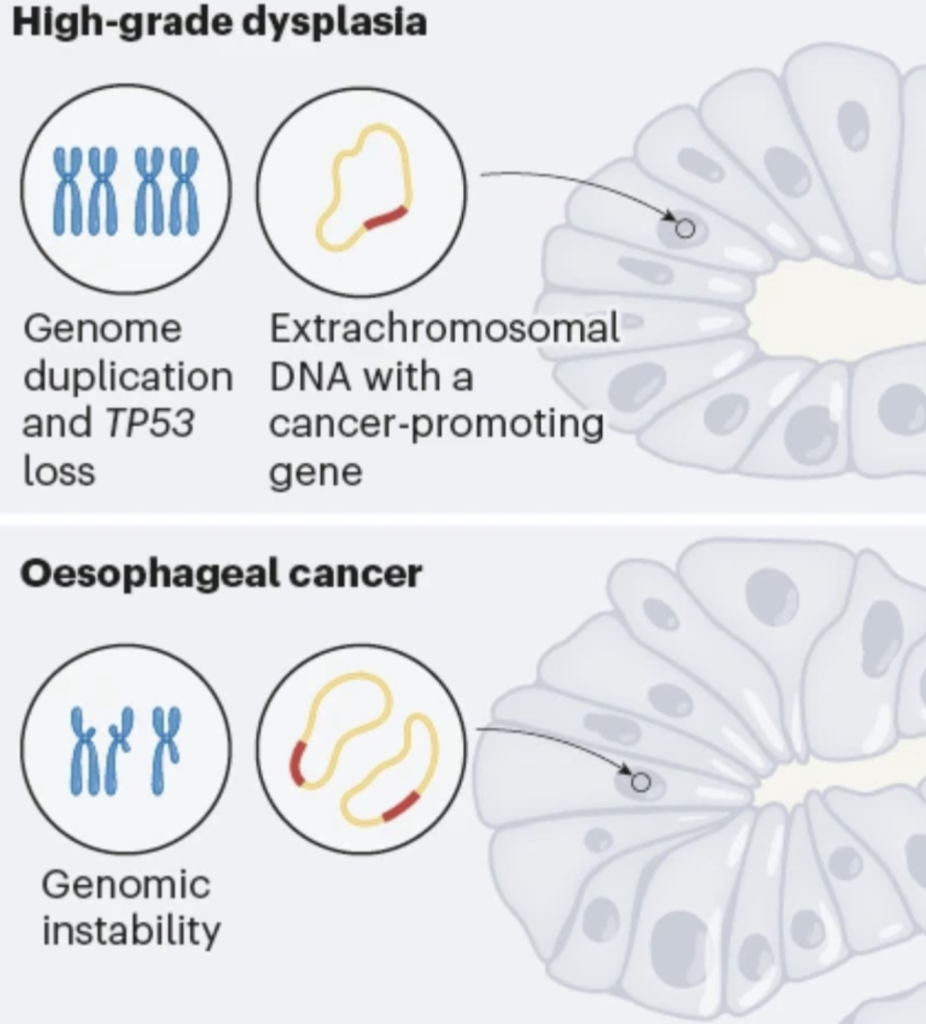
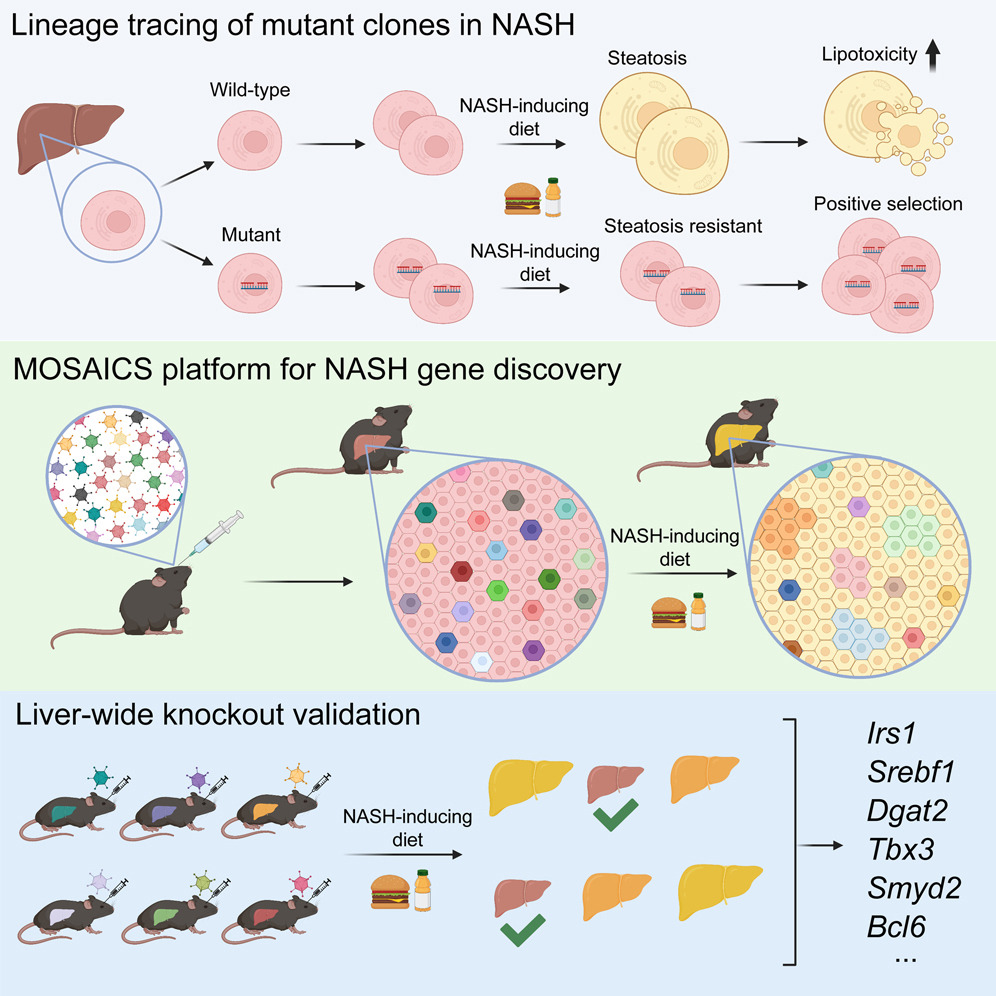
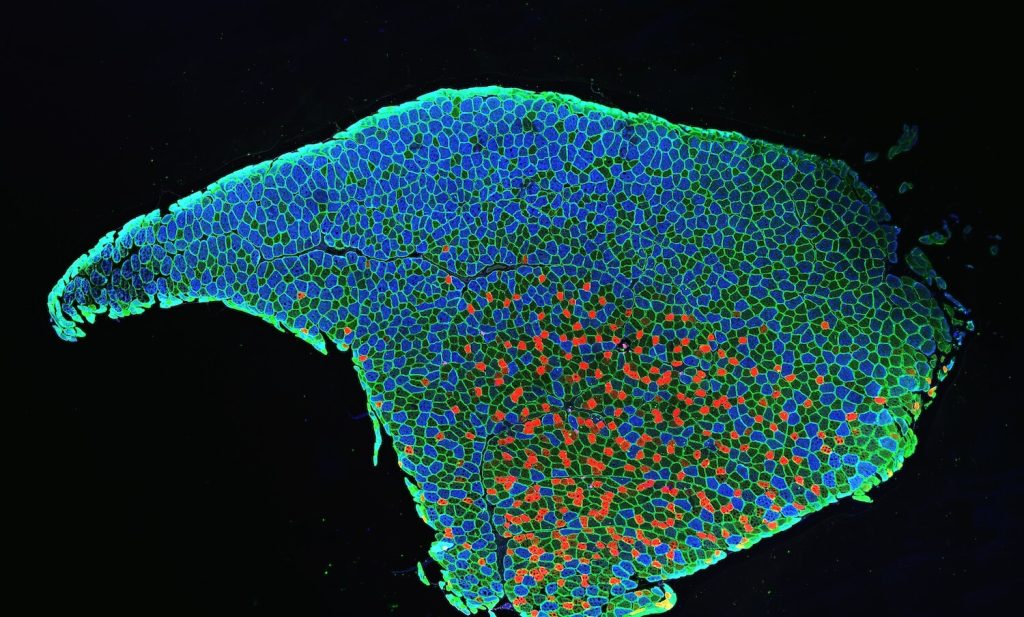
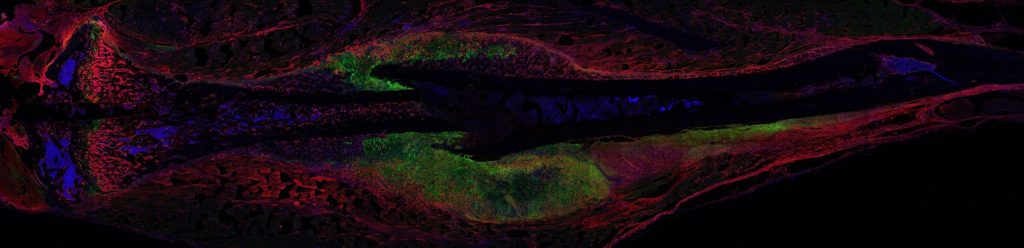
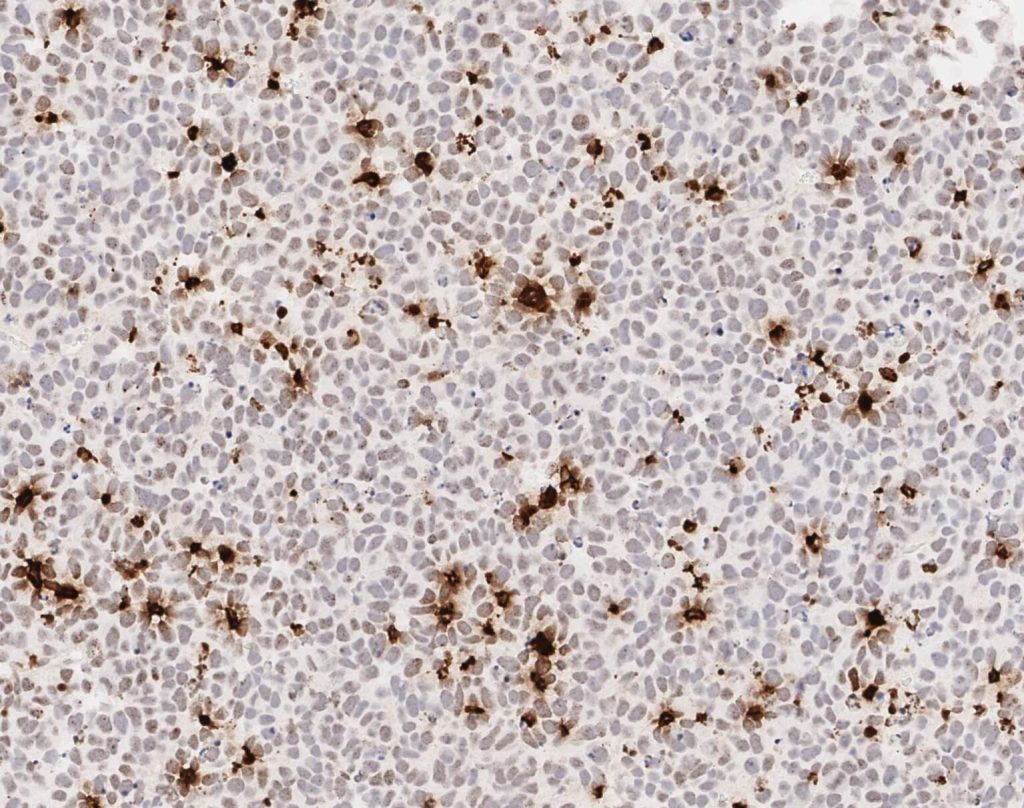
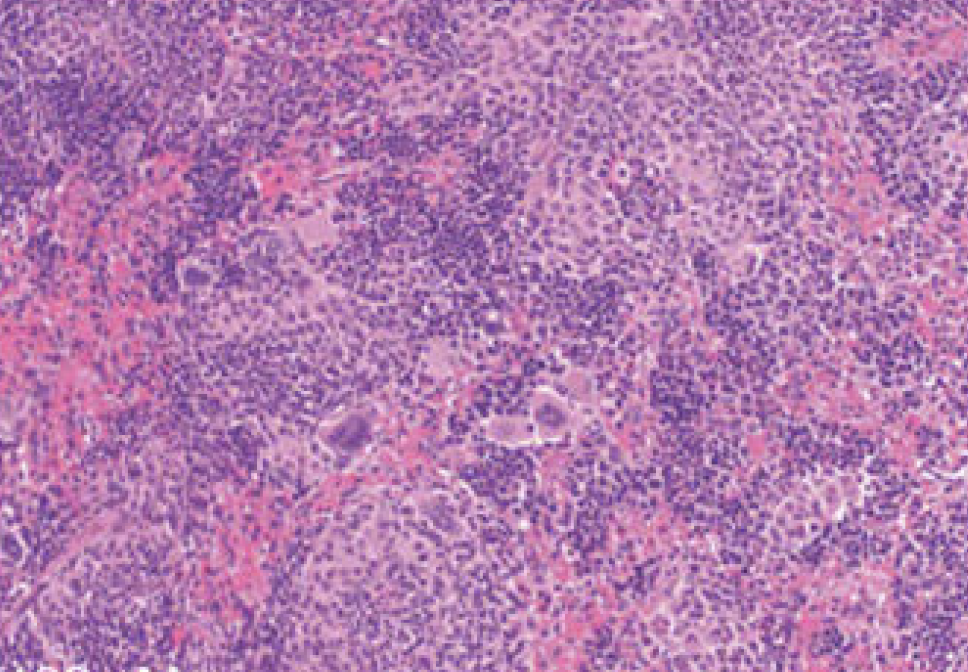
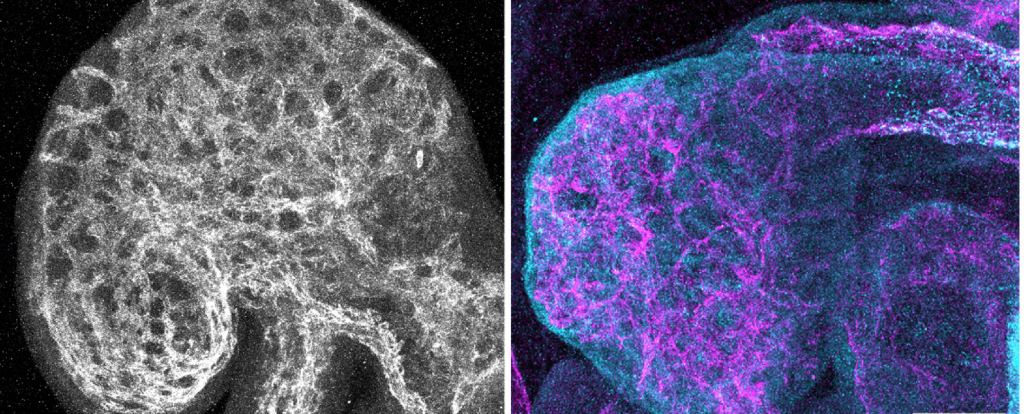
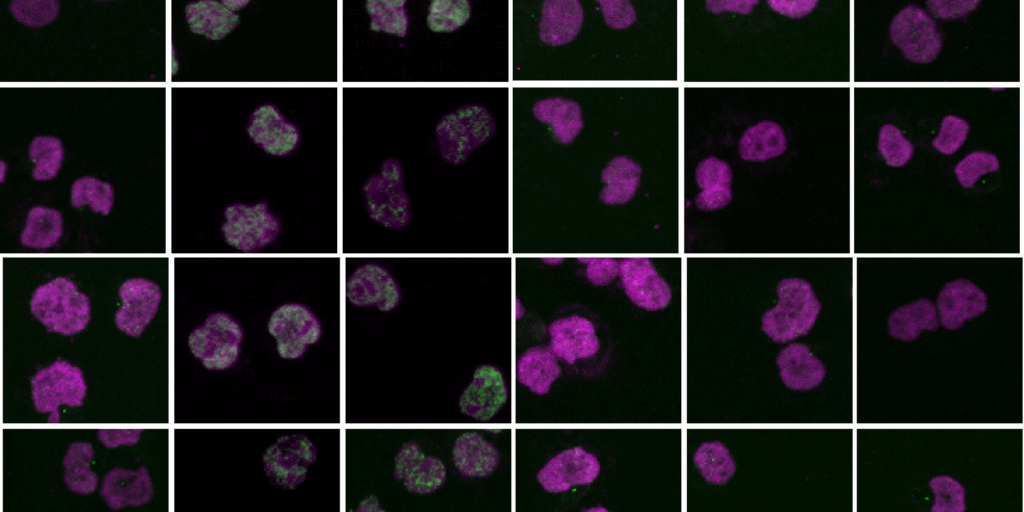
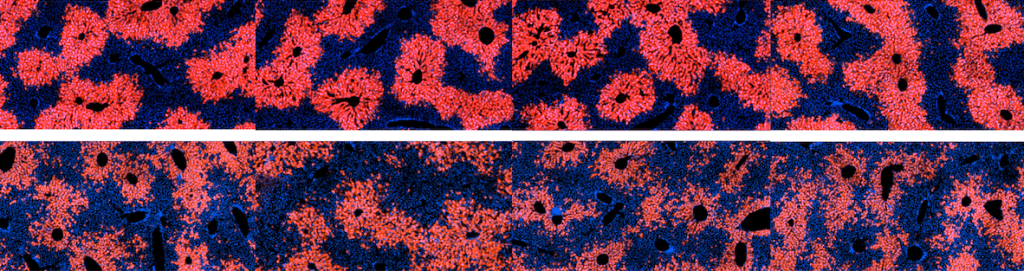
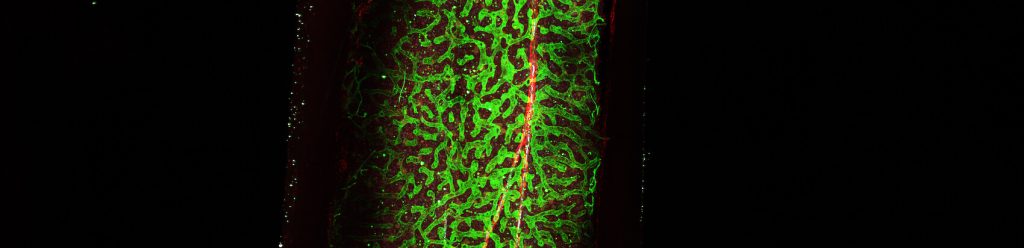
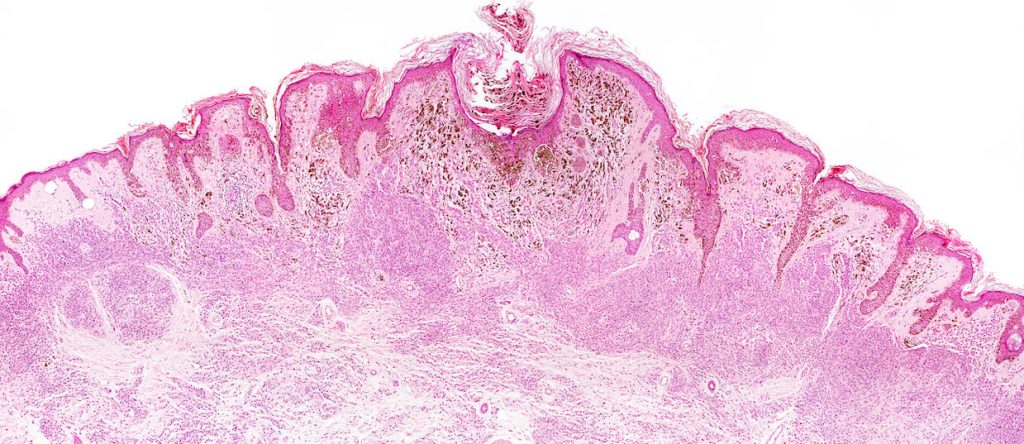
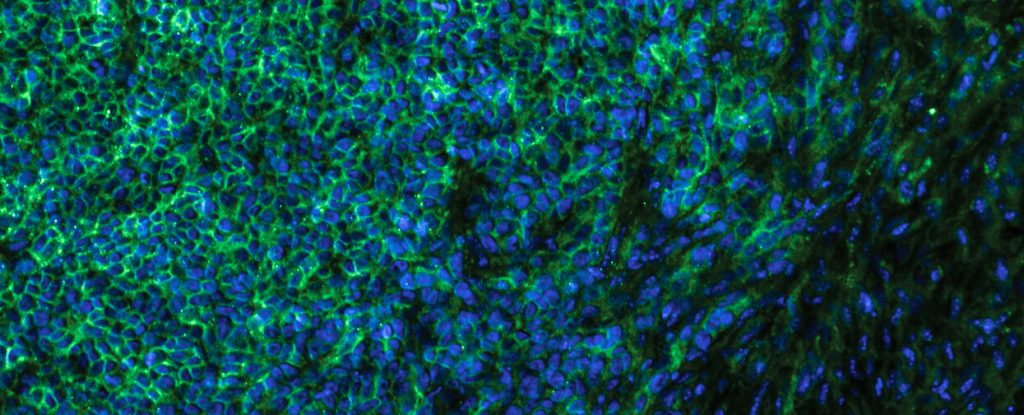
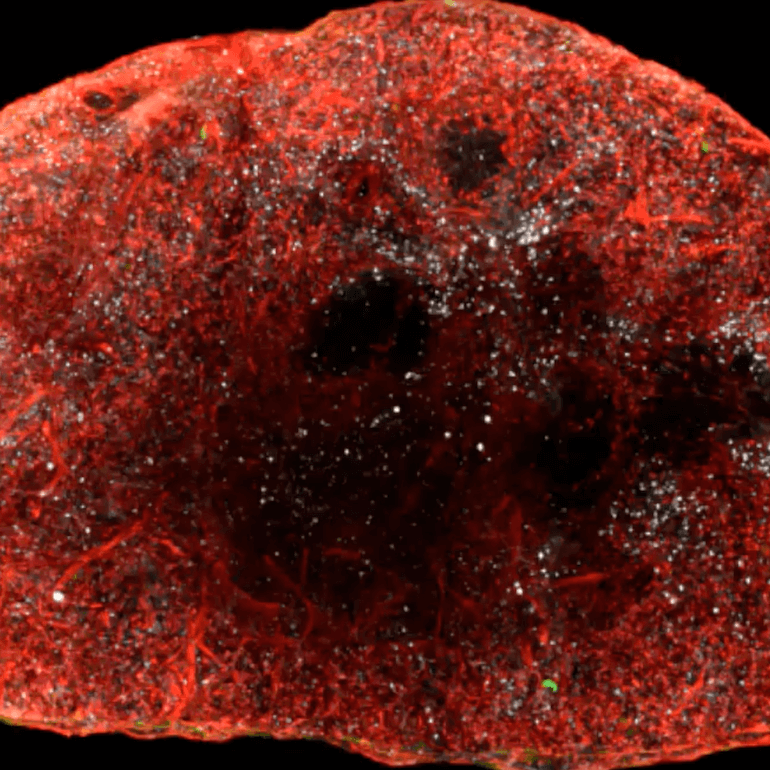
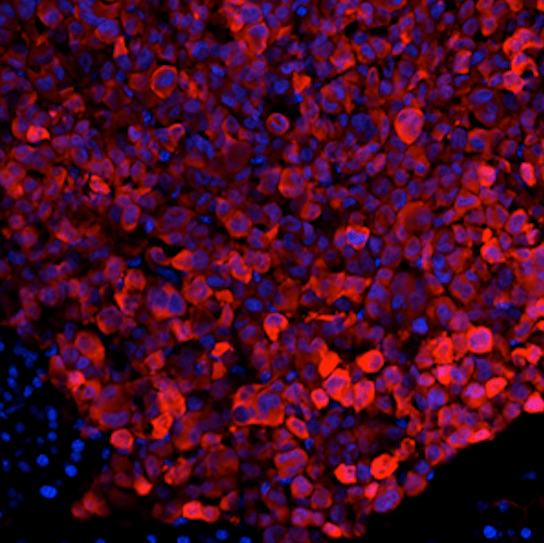
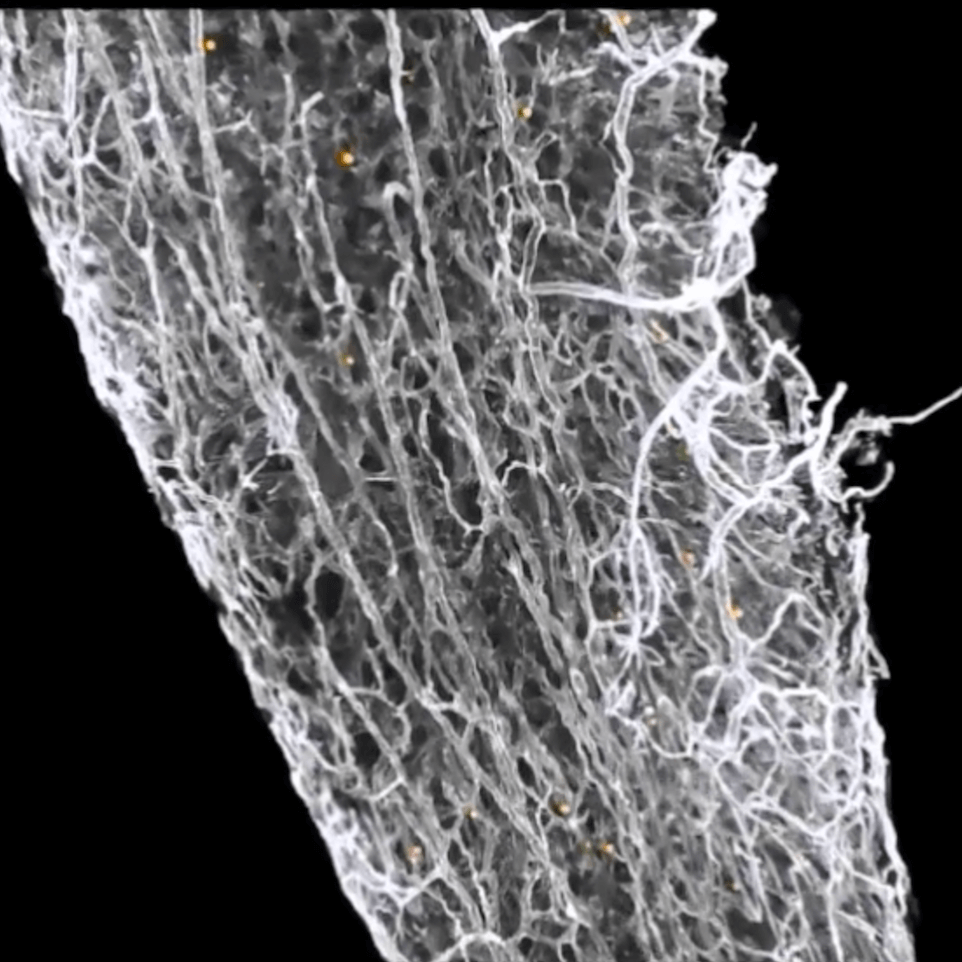
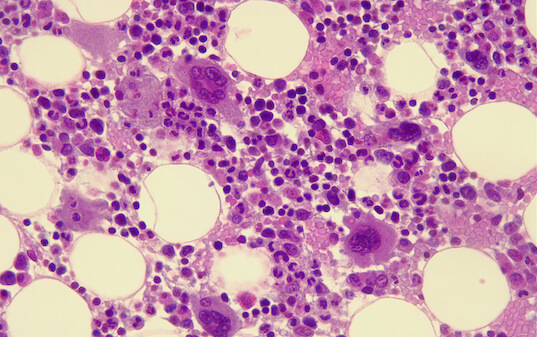
Cancer cells salvage purine nucleotides to fuel tumor growth, including purines in foods we eat, an important discovery with implications for cancer therapies. CRI researchers challenged the long-standing belief that tumors primarily acquire purine nucleotides – building blocks for DNA, which is required for cellular growth and function – by constructing them from scratch via de novo synthesis. Research also shows tumors significantly use the more efficient salvage, or recycling, pathway to acquire purines. Cell 187, 3602-18